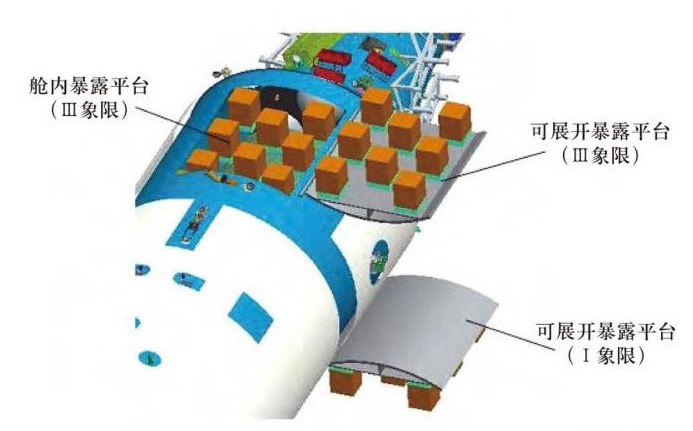
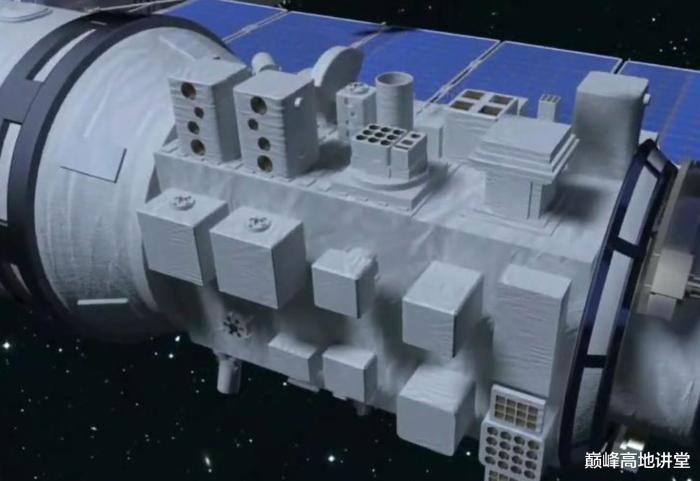
Next we look at the Mengtian (MT) aka space lab II. Similar to WT space lab, MT is divided into the work segment, cargo bay airlock segment, and resource segment. The work segment house the scientific experiment racks. Its unique feature is the cargo airlock bay.

The cargo airlock bay is equipped with an expose facility. After opening up, the expose facility provide an extended area to house experiment modules that need exposure to extreme environment including intense sun light, vacuum, heat, radiation, extreme temperature fluctuation etc. that are difficult to replicate on Earth. R&D applications include space material, electronic components, space biology, space physics etc. There're two expose facility, one on top, one at the bottom, both can be open or close as necessary.
Some experiments on the expose facility may need to be collected to return to Earth for further analysis. There're two methods to collect exposed experiment. The first involved EVA to collect the experiment sample.
In the EVA of the SZ-7 mission, Zai Zhigang collected an exposed experiment of solid lubricant material. Collecting exposed experiment sample through EVA is time consuming and inefficient.
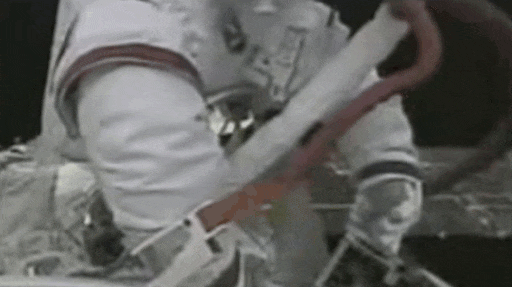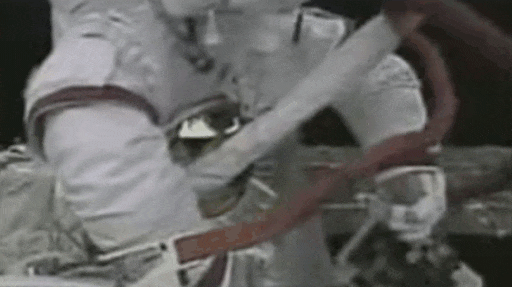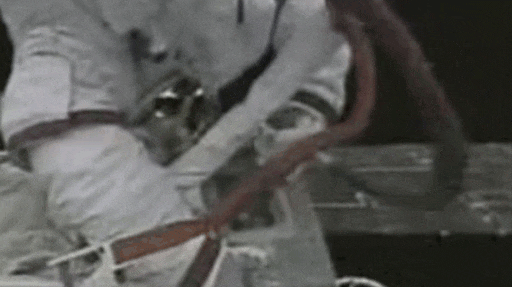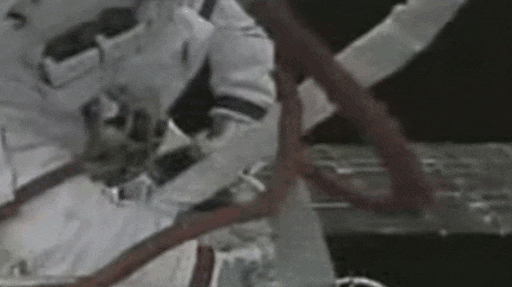
The second method implemented on the MT cargo airlock bay enable exposed experiments to be returned to the bay where astronauts have easy access to the exposed experiment modules.
The MT cargo bay expose facility in the open state during under water training session.
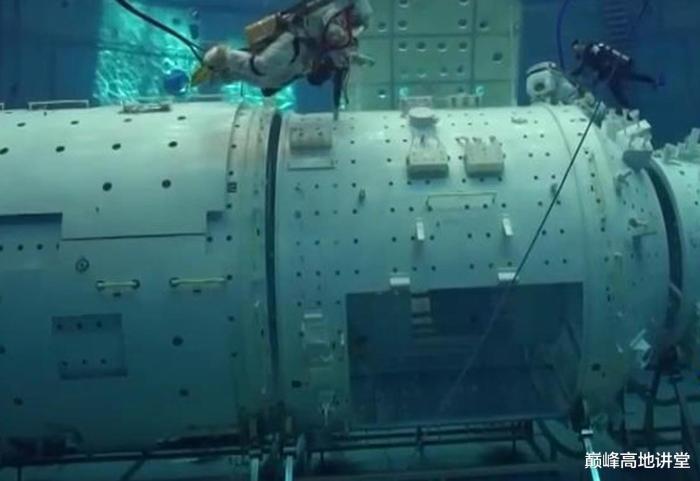

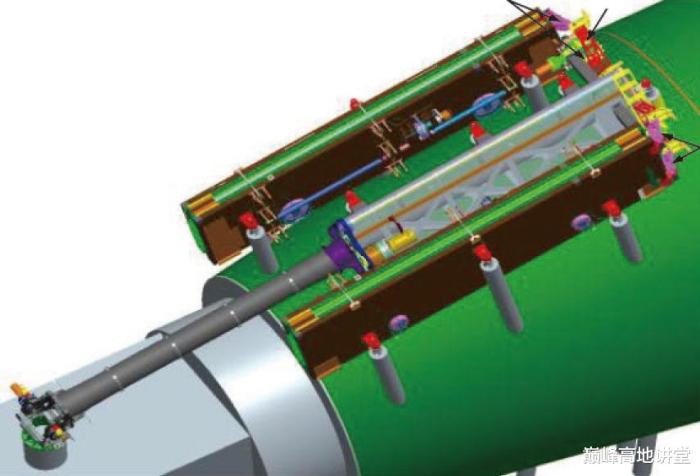
The cargo airlock bay is equipped to provide rotation, extension, position adjustment to the exposed experiment modules. The 5 m robotic arm is provided to further manipulate the exposed experiment module. Besides carrying out expose experiments, the cargo airlock bay will also be used for cargo transfer between CSS interior and exterior, nanosat launching, Earth observation etc. Both MT and WT space lab provide up to 67 mounting point for exterior payload, including mounting point for large size exterior payload.
Assemblying the scientific experiments on the rack.

Before the CSS, China has limited space exposure experiment resources available. With the CSS, booming space experiments demands will be met.
CSS Power Generation
CSS with close to 100 tons will house up to 25 scientific experiment racks, compared to 31 scientific experiment racks onboard the 400 ton ISS. Efficient power system is needed to meet the power demand to conduct the experiments in a smaller space station. CSS will have a sulphus power generation capacity.
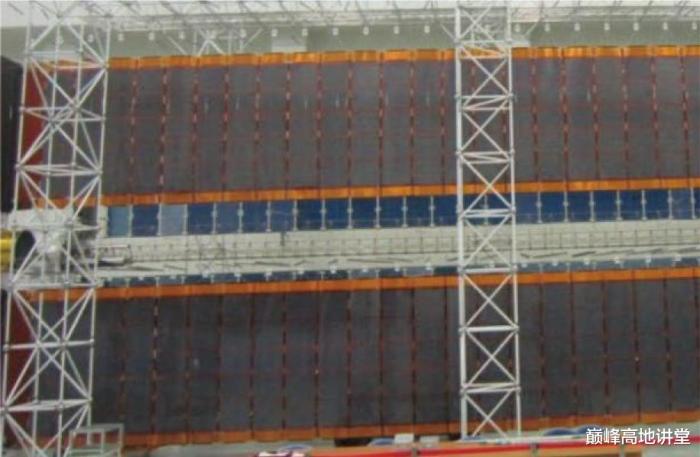
The resource segment of the WT and MT space lab are installed with high efficiency solar array wings. The soft solar panels are compressed during launch, and extend in space. The solar array wings on the space lab is far larger than the solar array wings on the Tianhe core module. As such, they will only be half extended during rendezvous with the Tianhe core module, and fully extended after transposed to their intended orientation.
Space lab solar array wings in compressed state.
Space lab solar array wings full extension after mounting at the side.
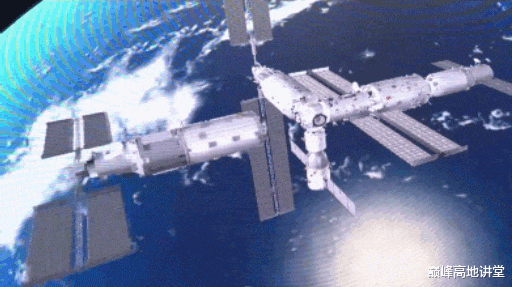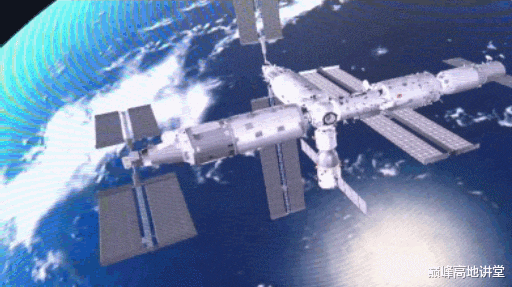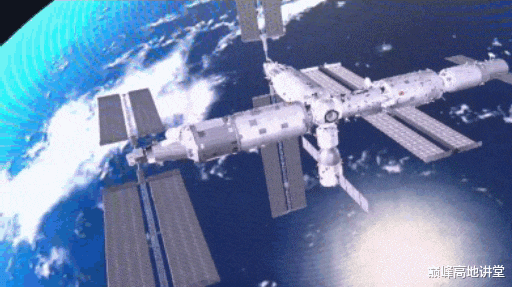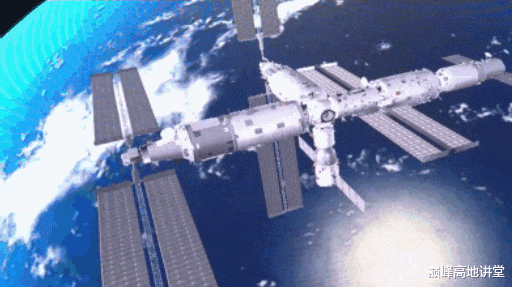
After the space labs are installed, the solar array wings on the Tianhe core module will be taken down at appropriate time and transfer to the tip of the space lab to maximize exposure to the sun, and thus power generation.
To complete the transfer, the Tianhe core module solar array wings will be first compressed, then astronauts detach it in EVA with the help of the robotic arm. The robotic arm will "carry" the detached solar array wings to the tip of the space lab where astronauts will complete its attachment to the space lab in EVA.
The solar array wings on the Tianhe core module is smaller relative to the solar array wings on the space lab modules.
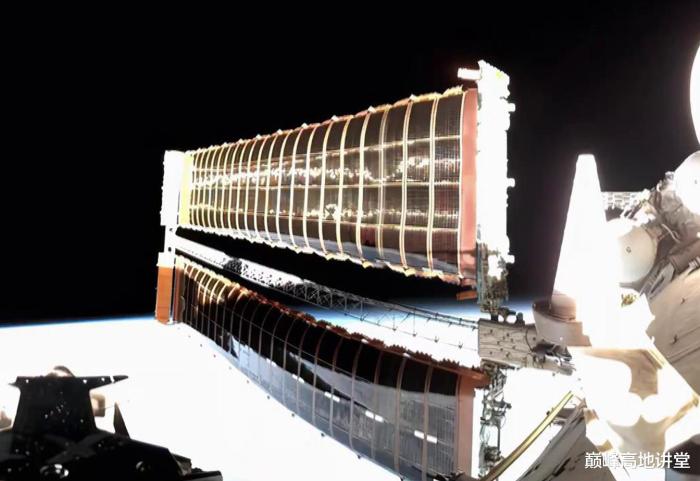

The transfer of the solar array wings will be carried out in a complicated EVA. Such transfer will be done for the first time in human space flight. Robotic arm moving the compressed and detached solar array wings is depicted below.

After the transfer, the Tianhe solar array wings will be installed at the tip of the space labs.

CSS will generate 0.41 kW per ton compared to 0.26 kW per ton of the ISS. In fact CSS has so much power sulphus that in the extended 180 ton CSS, the additional two space lab module won't be equipped with solar array wings at all. The current solar array wings combined is designed to support power requirement of the additional two space labs.
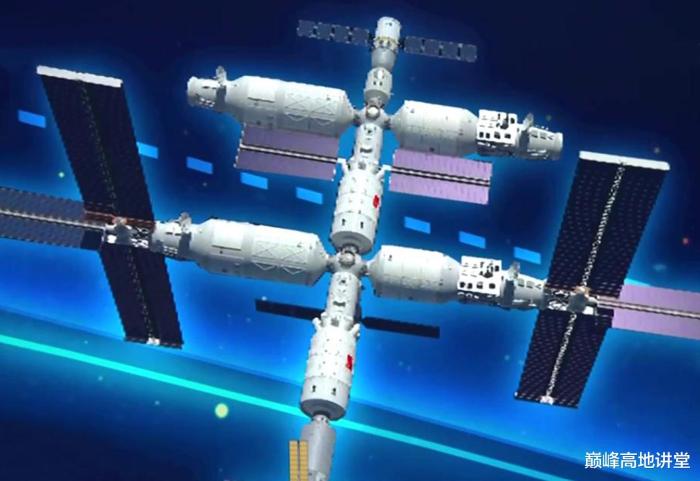
The Chinese human space flight project 921 started thirty years ago initially envisage a single moudle 20 ton space station that is both the core module and lab module. Space experiment capacity is very limited.
In the 21st century, a three module space station is proposed. The early space station is very different from the current CSS. In terms of solar array wings, it differ in three area:
It uses hard solar array panels, with increasing weights.
Every solar array wings are much smaller in size.
The arrangement of the solar array wings is different. A total of five equal size solar array wings, two on each space lab, three on the core module.The first three module Chinese space station concept.
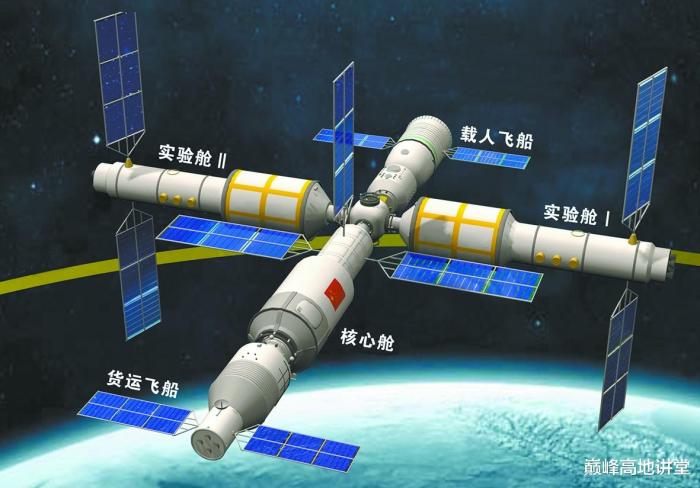

The soft solar array panel used in the current CSS.
